The Foreign Exchange Market, also known as Forex or the FX market, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with daily trading volumes reaching $4 trillion. Here are some basic facts and tips for those planning to trade in Forex currencies.
The Short History of the Foreign Exchange Market
The Forex market emerged during the 1970s following 30 years of government-imposed restrictions on foreign exchange transactions. The major event that triggered the creation of the Forex market was the collapse of the Bretton Woods Agreement. This agreement had established the global monetary system after World War II and remained in place for about 30 years. Under the Bretton Woods system, all major currencies were pegged to the US dollar, and gold reserves served as the foundation for the dollar’s value.
In the early 1970s, President Richard Nixon announced that the United States would no longer convert US dollars into gold. This led to the adoption of the floating exchange rate system, which soon became the global standard.
The Forex market came into existence as major countries gradually transitioned from fixed exchange rates under Bretton Woods to floating exchange rates.
Today, there are three (3) main exchange rate systems:
-
Floating rate – Exchange rates are determined by supply and demand. (This is the dominant system.)
-
Dollarisation – Some countries choose to link their exchange rate directly to the US dollar (e.g., Panama).
-
Pegged rate – Some countries opt to peg their currency to another currency, such as the euro or the Chinese yuan.
Key Characteristics of Today's Currency Market
Here are some fundamental characteristics of the modern Foreign Exchange market:
-
24-hour operation, 5 days a week – The market operates continuously from Sunday at 20:15 GMT to Friday at 22:00 GMT.
-
Overnight rate mechanism (SWAPS) – This mechanism balances the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a trade. It can result in either a positive or negative impact on your portfolio balance.
-
Massive capital liquidity through the ECN network – The Electronic Communication Network (ECN) enables fast and transparent trading with deep liquidity.
-
Very tight spreads on currency pairs – Major currency pairs, such as the Eurodollar, can be traded with spreads as low as 0.2 pips (equivalent to 0.0002 in the EUR/USD exchange rate).
-
Low margin requirements and high leverage options – Traders can access high leverage, up to 30:1 in the EU, with relatively low initial capital requirements.
-
Global reach and round-the-clock sessions – Forex trading spans across major global financial centers, with three primary trading sessions: American, European, and Asian. London remains the largest Forex hub in the world.
Forex Market Participants
The Forex market consists of a wide range of participants, each playing a unique role:
-
Central Banks (Monetary Authorities) – They intervene in the currency markets to control inflation, stabilize the national currency, or support economic policy.
-
Commercial and Investment Banks – These institutions facilitate currency trading for clients and engage in speculative trading on their own behalf.
-
Large Trade Companies (Importers/Exporters) – These companies exchange currencies to conduct international business and manage currency risk.
-
Institutional Investors – This includes hedge funds, investment firms, and pension funds that trade large volumes of currency as part of their global investment strategies.
-
Forex Brokers and Dealers – Brokers provide access to the Forex market for institutional and retail clients, often through electronic trading platforms.
-
Retail Traders and Tourists – Individual traders participate for speculative purposes, while tourists exchange currencies for travel and personal use.
Three Trading Sessions
There are three main Forex trading sessions in both the winter and summer time zones:
|
Forex Time Zone |
GMT (open-close) |
EST (open-close) |
|
| Winter Time Zone (October to April) |
|
1:00 PM |
8:00 AM |
|
8:00 AM |
3:00 AM |
|
|
12:00 AM |
7:00 PM |
|
| Summer Time Zone (April to October) |
|
12:00 PM |
8:00 AM |
|
7:00 AM |
3:00 AM |
|
|
12:00 AM |
8:00 PM |
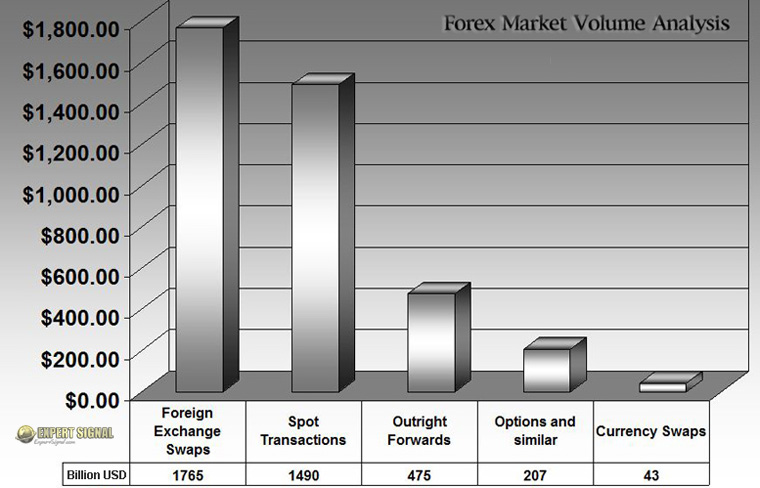
Forex Volume Analysis
The liquidity and trading volume in the currency market are enormous. Below is a typical breakdown of the $4 trillion daily Forex market volume:
-
$1.765 trillion – Foreign exchange swaps
-
$1.490 trillion – Spot transactions
-
$0.475 trillion – Outright forwards
-
$0.207 trillion – Options and other derivative products
-
$0.043 trillion – Currency swaps
Chart: Distribution of daily Forex trading volumes

Currency Pairs
Currencies are always traded in pairs, categorized as major, minor, or exotic pairs. Each Forex pair is quoted in units of the quote currency. The first currency in the pair is called the base currency, and the second is the quote (or counter) currency — formatted as BASE/QUOTE.
While hundreds of currency pairs exist, about 85% of total trading volume comes from the following major pairs:
-
EUR/USD – Euro / US Dollar
-
GBP/USD – British Pound / US Dollar
-
USD/JPY – US Dollar / Japanese Yen
-
USD/CAD – US Dollar / Canadian Dollar
-
AUD/USD – Australian Dollar / US Dollar
-
USD/CHF – US Dollar / Swiss Franc
Trading these pairs offers high liquidity and typically involves very tight spreads (the spread is the difference between the ask and bid prices).
Most Traded Currencies in the Foreign Exchange Market
The majority of Forex trading involves just 18 currencies. Among them, the eight most-traded currencies are:
-
U.S. Dollar (USD) – By far the dominant currency
-
Euro (EUR) – European Union
-
British Pound (GBP) – United Kingdom
-
Japanese Yen (JPY) – Japan
-
Swiss Franc (CHF) – Switzerland
-
Canadian Dollar (CAD) – Canada
-
Australian Dollar (AUD) – Australia
-
New Zealand Dollar (NZD) – New Zealand
What Moves Forex Currencies
Like all financial assets, exchange rates are driven by supply and demand. A key to understanding the Forex market is grasping the central role of the U.S. Dollar. When global demand for the dollar increases, its value rises relative to other major currencies.
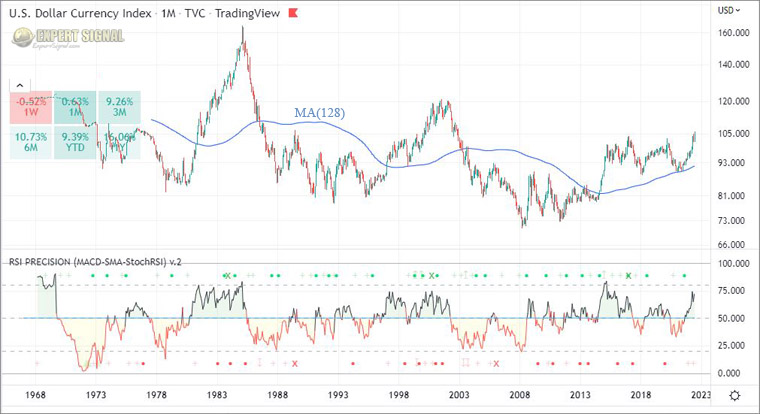
TIP: Use the U.S. Dollar Currency Index (DXY) chart to observe trends and cyclic patterns in the dollar’s performance.
You can find the DXY chart on TradingView.
In the following monthly chart: the US Dollar Index (DXY) is shown along with the MA(128) and the free RSI Precision indicator by G.P.
Chart: US Dollar Index (DXY) with the RSI Precision Indicator
In general, the demand for a particular currency is influenced by:
-
Monetary policies – Especially interest rate levels set by central banks
-
New macroeconomic data – Such as unemployment figures, inflation rates, consumer spending, and GDP growth
-
Overall business conditions – Reflecting the economic climate and investor sentiment
-
New legislation – Including changes in taxes, tariffs, or regulations affecting capital flows
-
Political, social, and strategic risks – Events or uncertainties that may impact investor confidence or economic stability
Key Forex Trading Tips
Forex trading is driven by fundamental factors and macroeconomic cycles. Only traders who make informed decisions and follow them with discipline can benefit from the fluctuations in the Foreign Exchange market. To trade Forex successfully, you need three essentials: skills, a trading strategy, and a money management system.
Below are some simple but essential trading tips for all Forex traders:
Forex Tip 1: Identify Your Trading Profile and Choose a Strategy That Suits Your Personality
Before selecting a trading strategy, you must answer these four questions:
-
What are your trading skills?
-
How much capital can you afford to lose?
-
What annual profit do you aim to achieve?
-
How much time can you dedicate weekly?
Answering these questions will help determine the best trading approach for your needs. Here are some examples:
-
Manual day trading requires a lot of time and carries significant risk.
-
Automated day trading requires strong technical skills and also involves high risk but less time.
-
Swing trading is less risky and more time-flexible.
-
Long-term trading requires minimal time and suits the average retail trader, though it typically yields lower returns.
Forex Tip 2: Don’t Use Multiple Strategies in the Same Account
Implementing multiple strategies in one account can be confusing, time-consuming, and risky. It’s better to focus on optimizing one strategy at a time. If you choose to apply multiple strategies, never run them in the same trading account. Even expert-level money management cannot fully protect against unexpected market events.
Case in Point:
In January 2015, the Swiss National Bank (SNB) unexpectedly abandoned its currency peg to the euro. The EUR/CHF pair crashed by around 20% in one day. Traders who were heavily leveraged and long on EUR/CHF saw catastrophic losses.
Lesson: Use separate accounts for different strategies. Black swan events can and do happen.
Forex Tip 3: Don’t Get Emotional About Your Trades
Human beings are naturally emotional—but emotions and trading don’t mix well. Trading success depends on logical thinking, discipline, and emotional control.
-
Don’t let greed push you to increase your position sizes after a few winning trades.
-
Diversify your trades and control risk by allocating only a small portion of capital to each position.
-
Understand that every strategy and every trader will face losing streaks. Stay consistent, and focus on identifying when your strategy is in or out of sync with the market.
Forex Tip 4: Keep a Record of All Your Trades
Maintaining a clear and honest trading journal is critical for long-term success.
-
A trade log helps you evaluate the effectiveness of your strategies and money management systems.
-
It allows you to analyze your performance over different time periods and avoid trading during historically unprofitable periods.
Forex Tip 5: Limit Your Greed, Leverage, and Position Sizes
Greed is one of a trader’s worst enemies. Trying to squeeze every last drop from the market often leads to bad decisions. Smart traders take what the market offers and patiently wait for the next opportunity.
-
High leverage increases both your potential gains and your risk—and also raises transaction costs.
-
Avoid "get-rich-quick" mindsets. Preserve your capital by using moderate leverage and keeping position sizes small.
Golden Rule: You can’t make money if you lose all your money in a few bad trades. -Poor risk management = eventual failure.
Forex Tip 6: Use the Right Order Types
Order placement is as important as trade selection. A well-timed order with proper sizing can make the difference between a good trade and a bad one.
-
Your stop-loss and take-profit levels should justify the risk–reward ratio.
-
Avoid trades with a reward-to-risk ratio of less than 3:1.
-
Don’t use overly tight stop-loss orders unless you’re an experienced scalper.
-
Consider trailing stops to lock in profits as trades move in your favor.
-
Be cautious during news releases—brokers may widen spreads or engage in stop-hunting during volatile moments.
Forex Tip 7: Choose the Right Broker for Your Needs
Selecting a reliable Forex broker is as important as choosing a solid trading strategy. Consider the following when choosing your broker:
-
Ensure the broker has been in business for at least five years.
-
Review their services and confirm they offer your preferred funding options.
-
Understand all costs involved—spreads, commissions, overnight fees, and transaction charges.
-
Start with a demo account, then move to a micro-lot account before scaling up.
-
As you gain experience, use an ECN/STP broker that offers tight spreads, fast execution, and a wide range of currency pairs.
-
If you're planning to apply swing or carry trading strategies, choose a broker that offers competitive overnight (SWAP) rates.
► Compare ECN/STP Foreign Exchange Brokers
■ Currency Trading
MORE ON ExpertSignal
| ■ COMPARE | » Cryptocurrency Accounts | » Expert Advisors | |||
| ■ FOREX SIGNALS | » EA Builder | » StrategyQuant (Algo) | » 1000pip Climber System | » 1000Pip Builder | |
| ■ TUTORIALS |